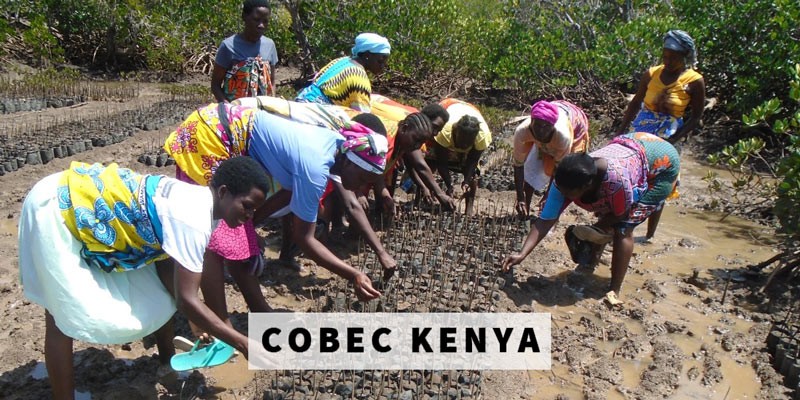
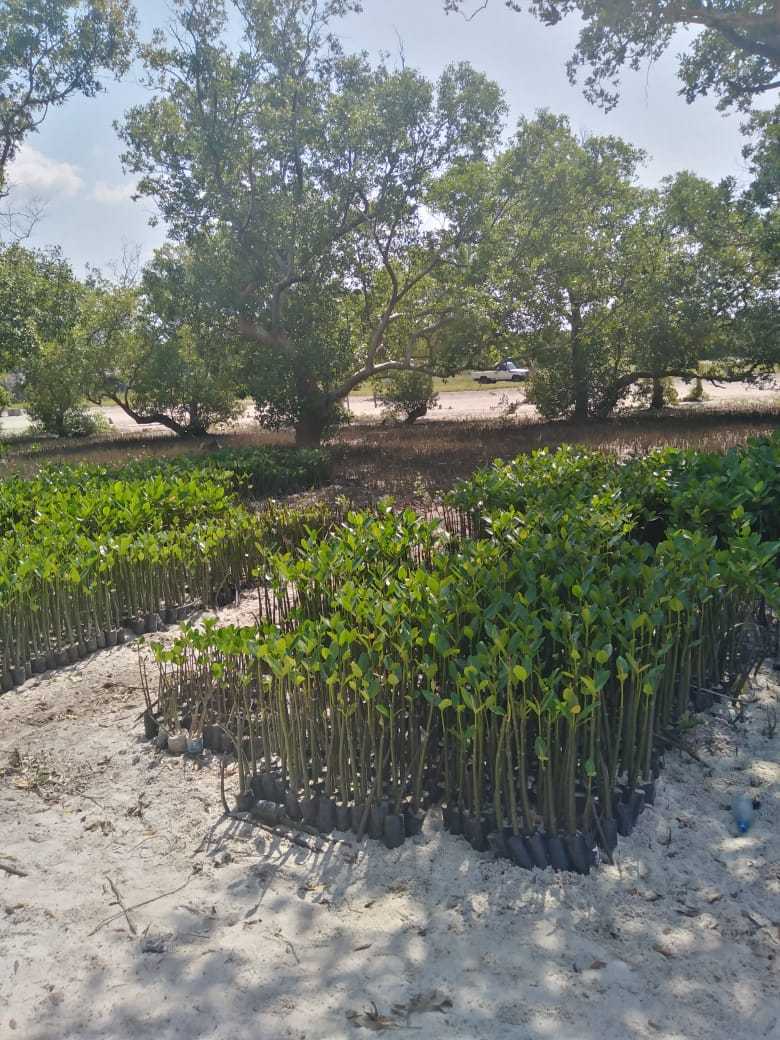
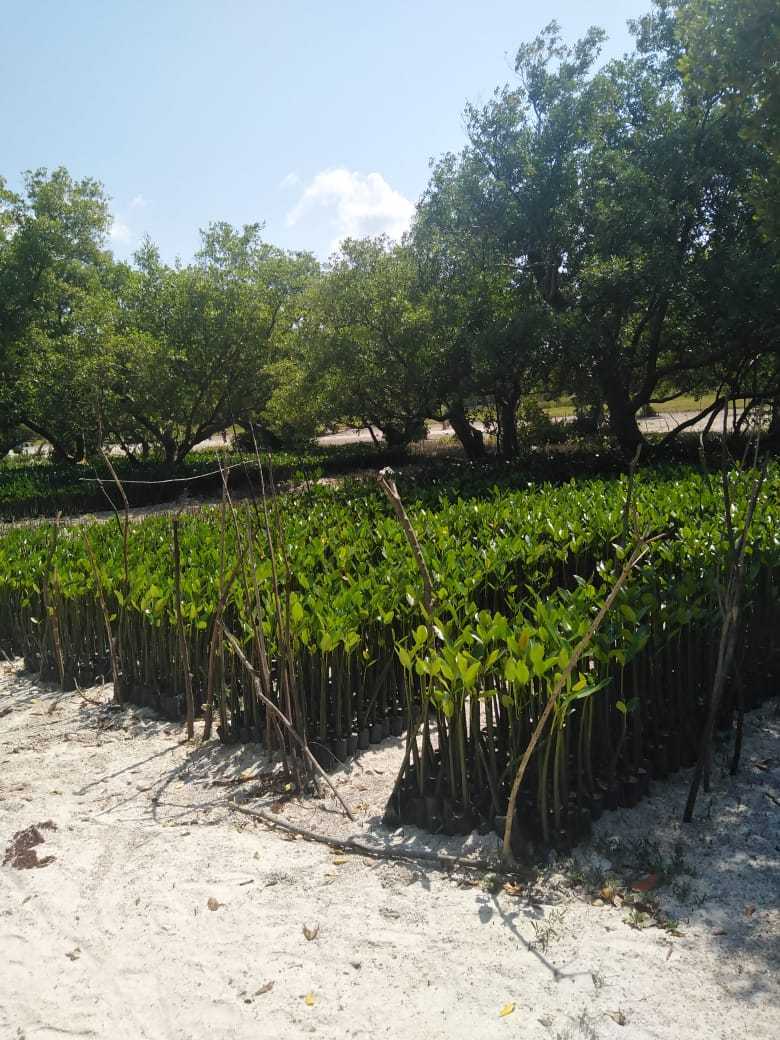
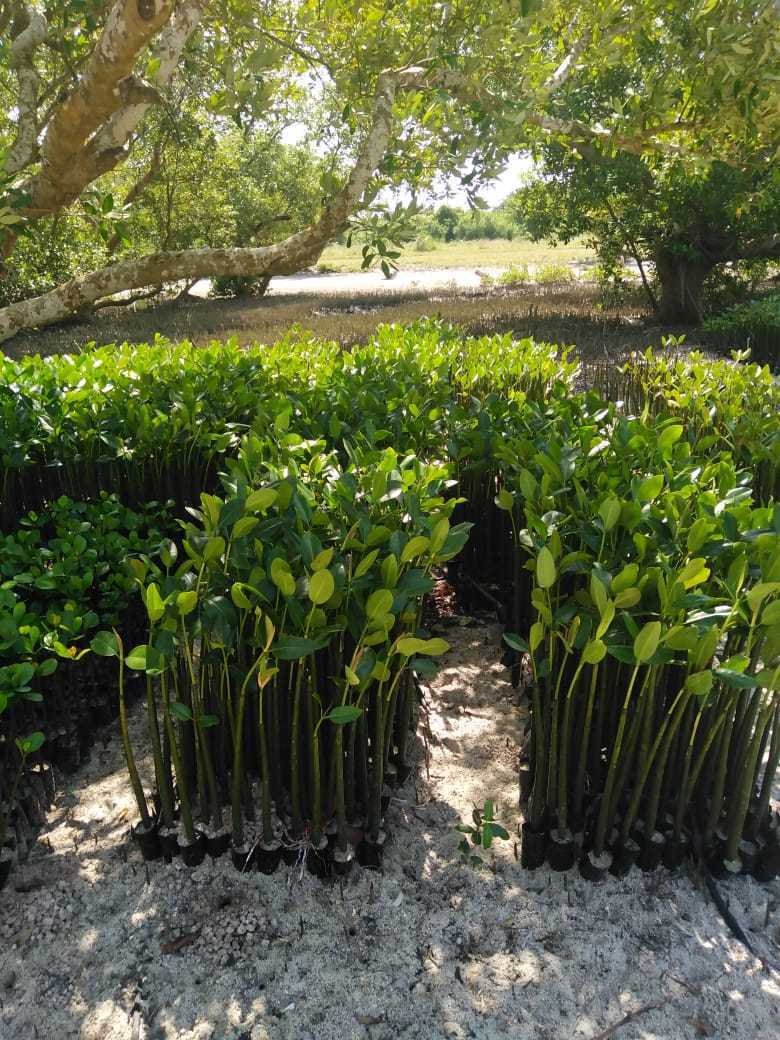
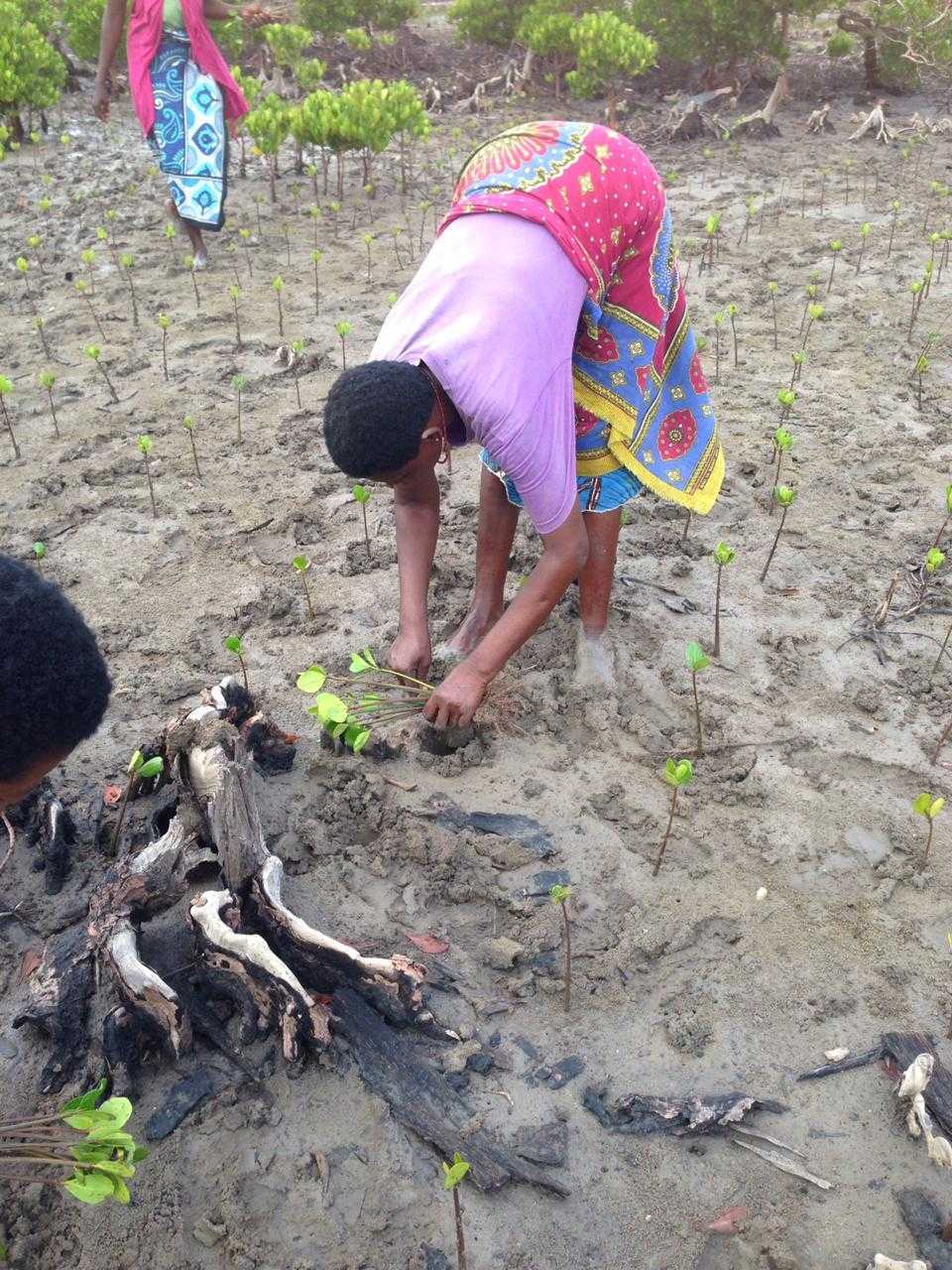
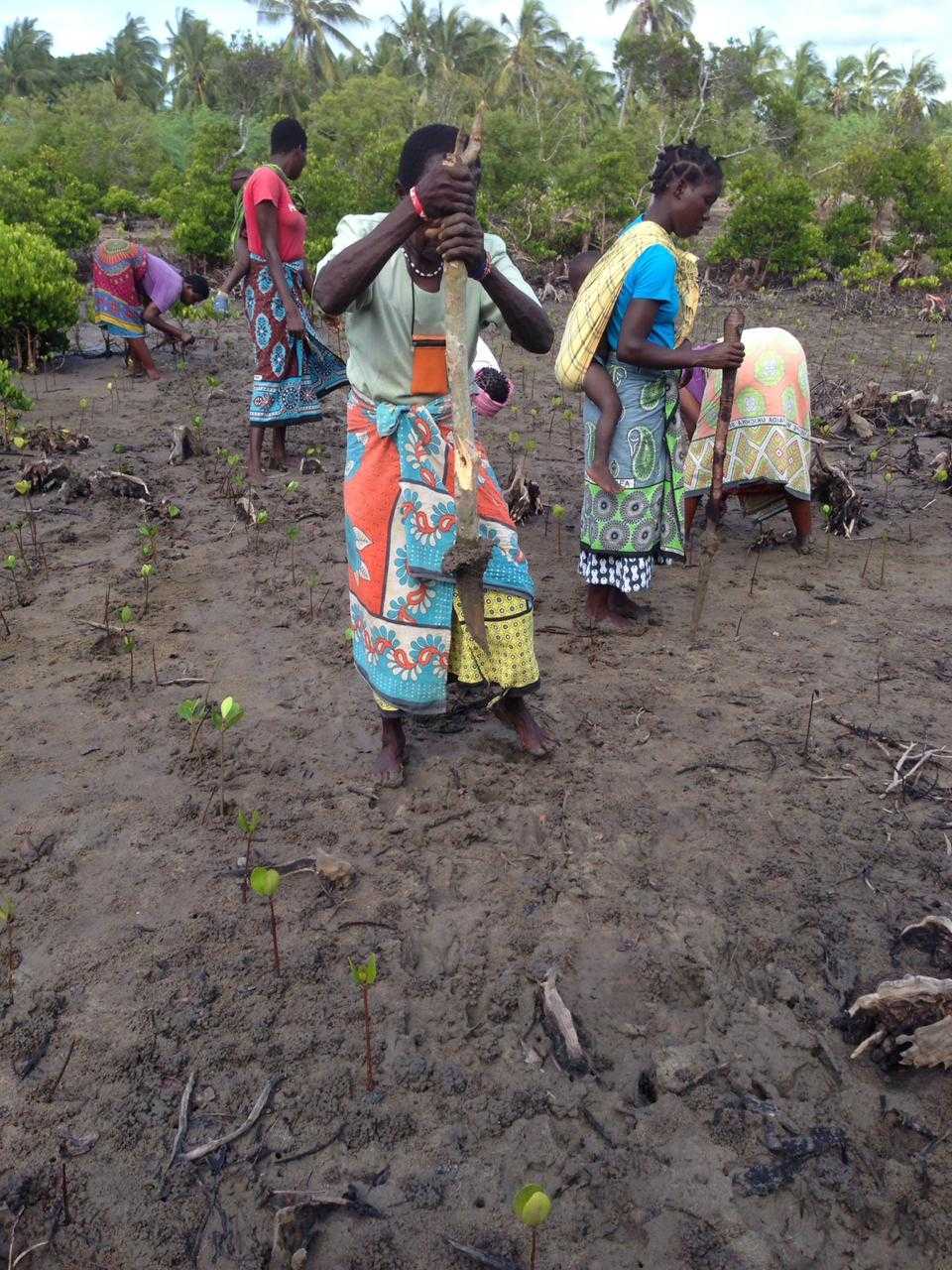
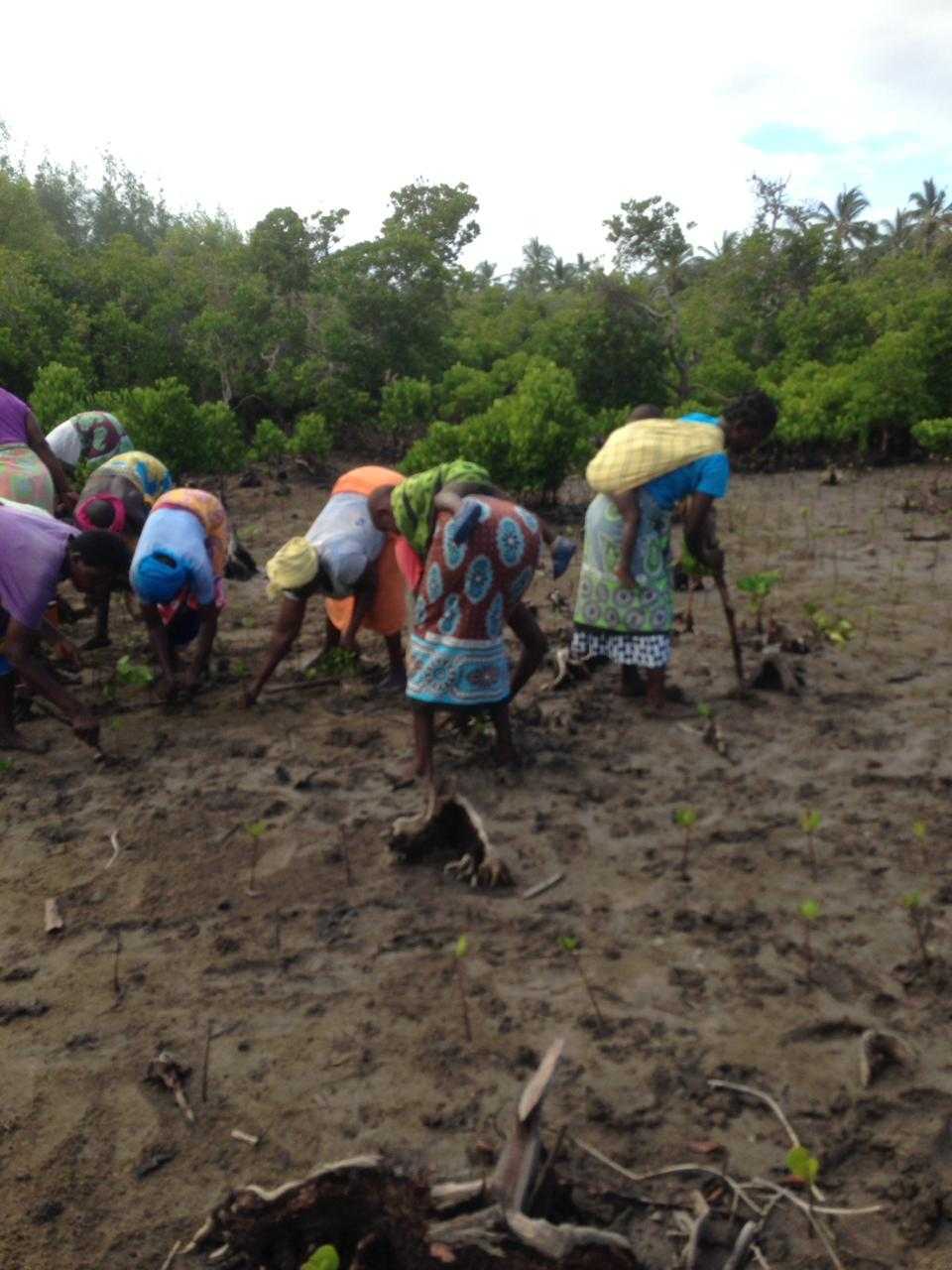
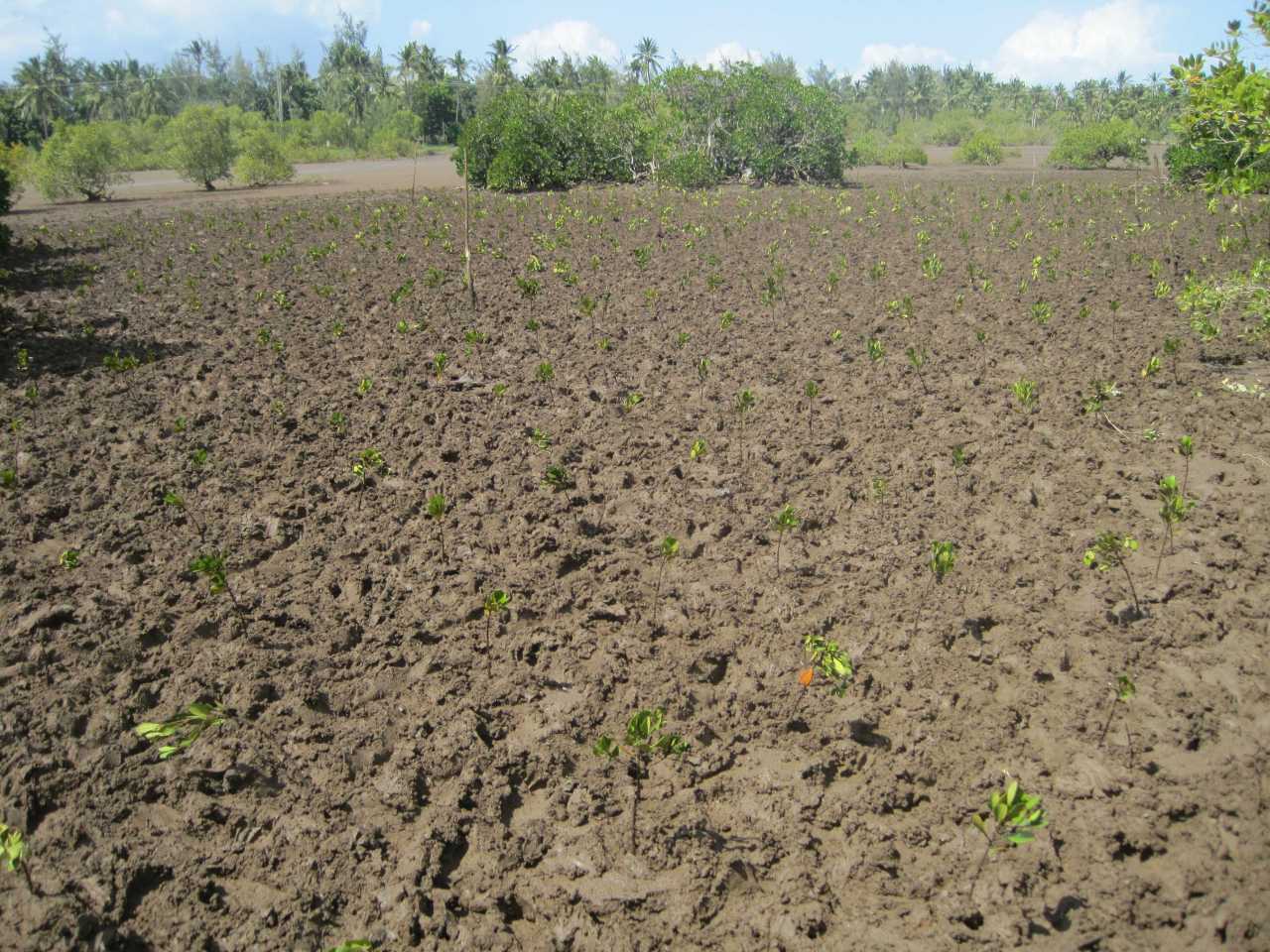
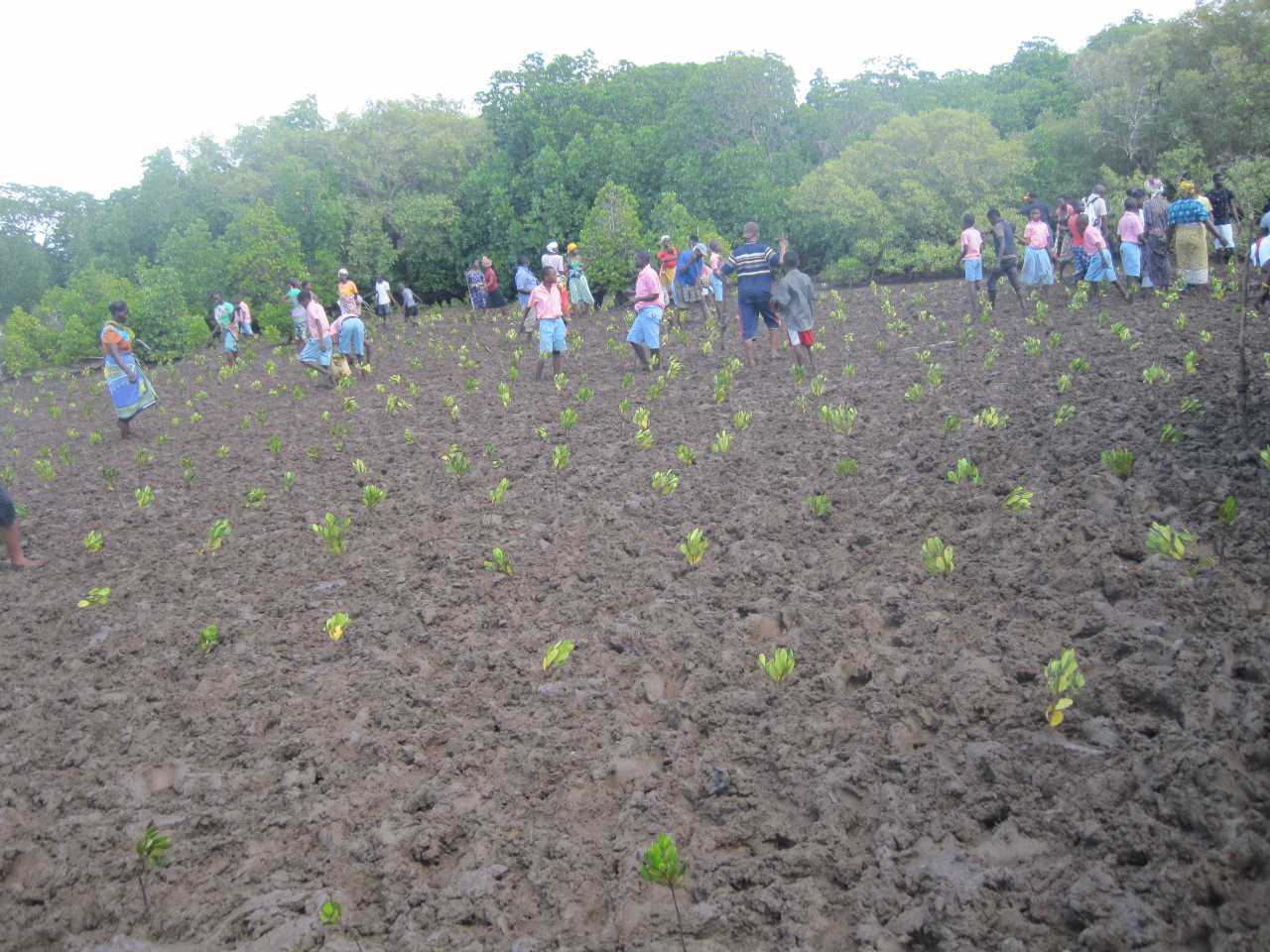
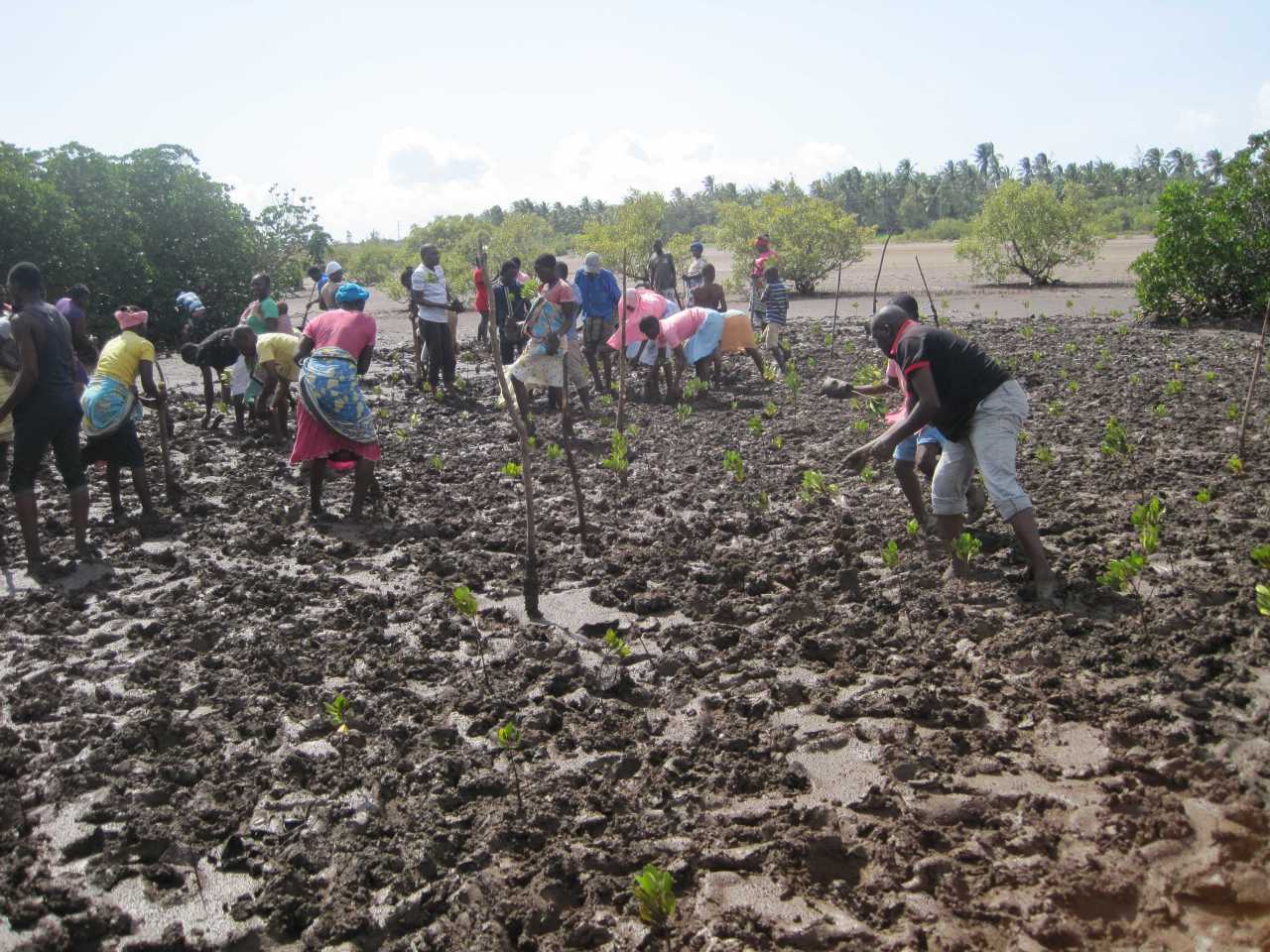
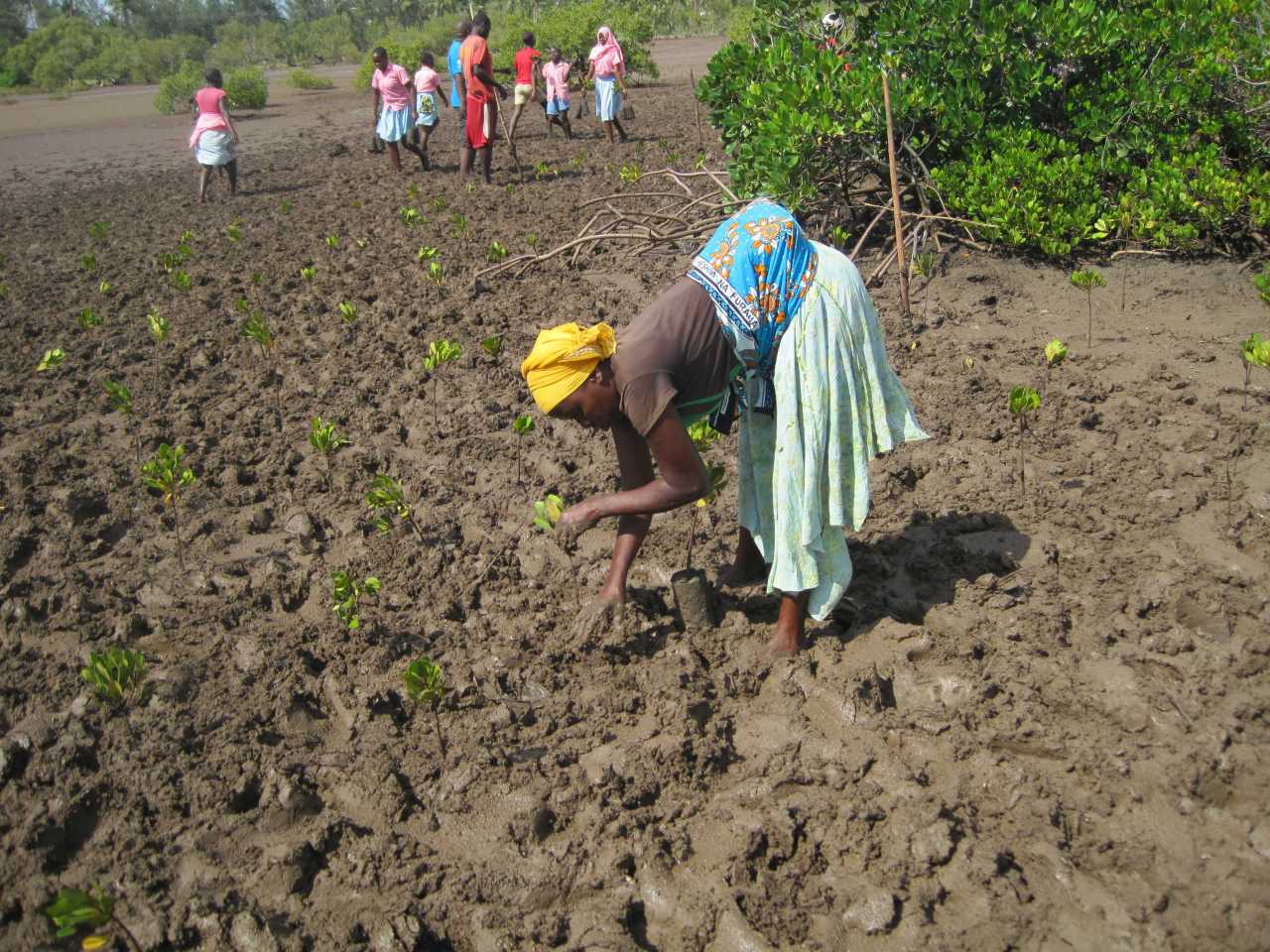
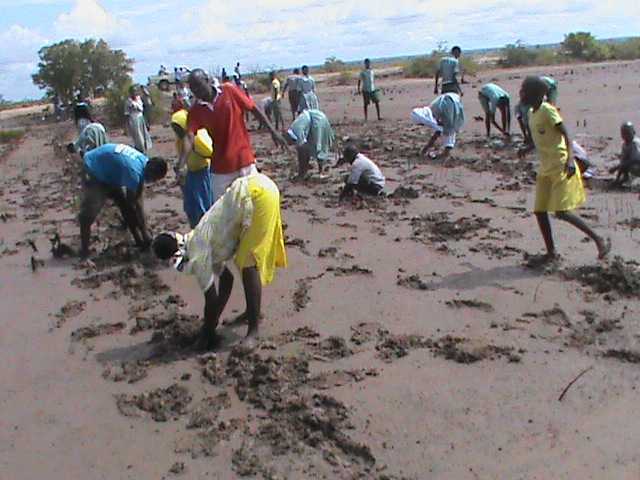
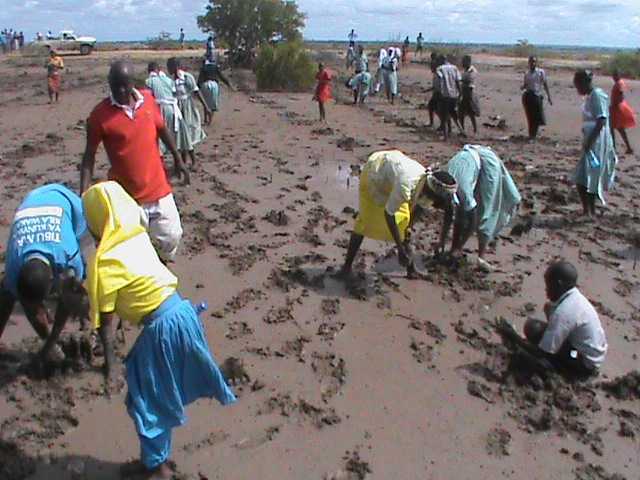
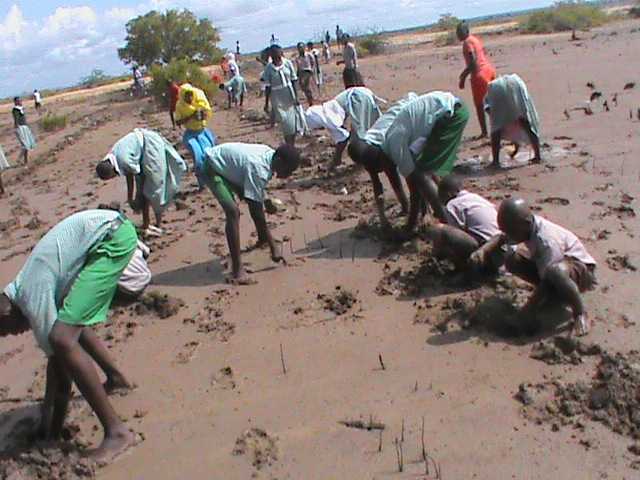
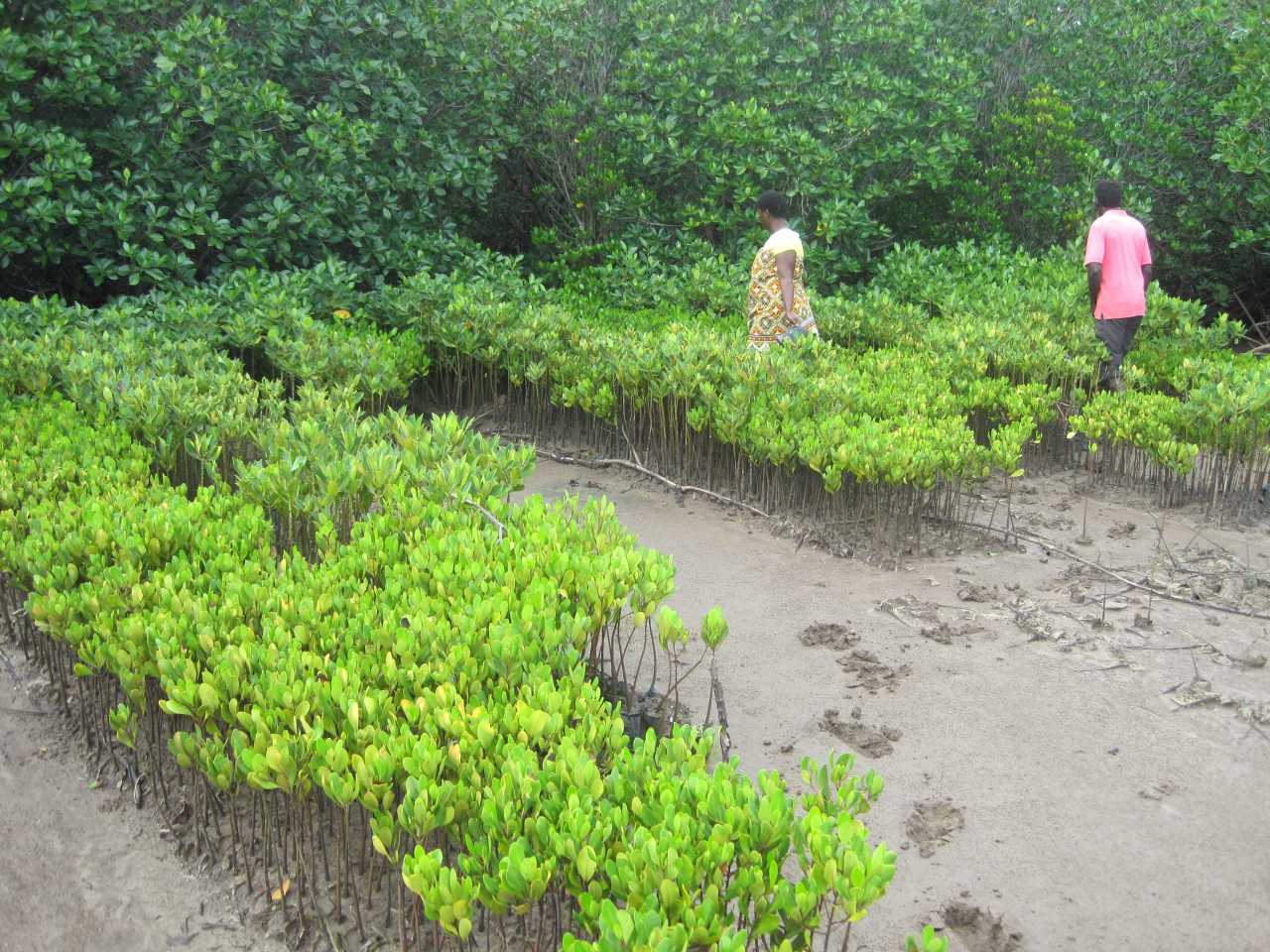
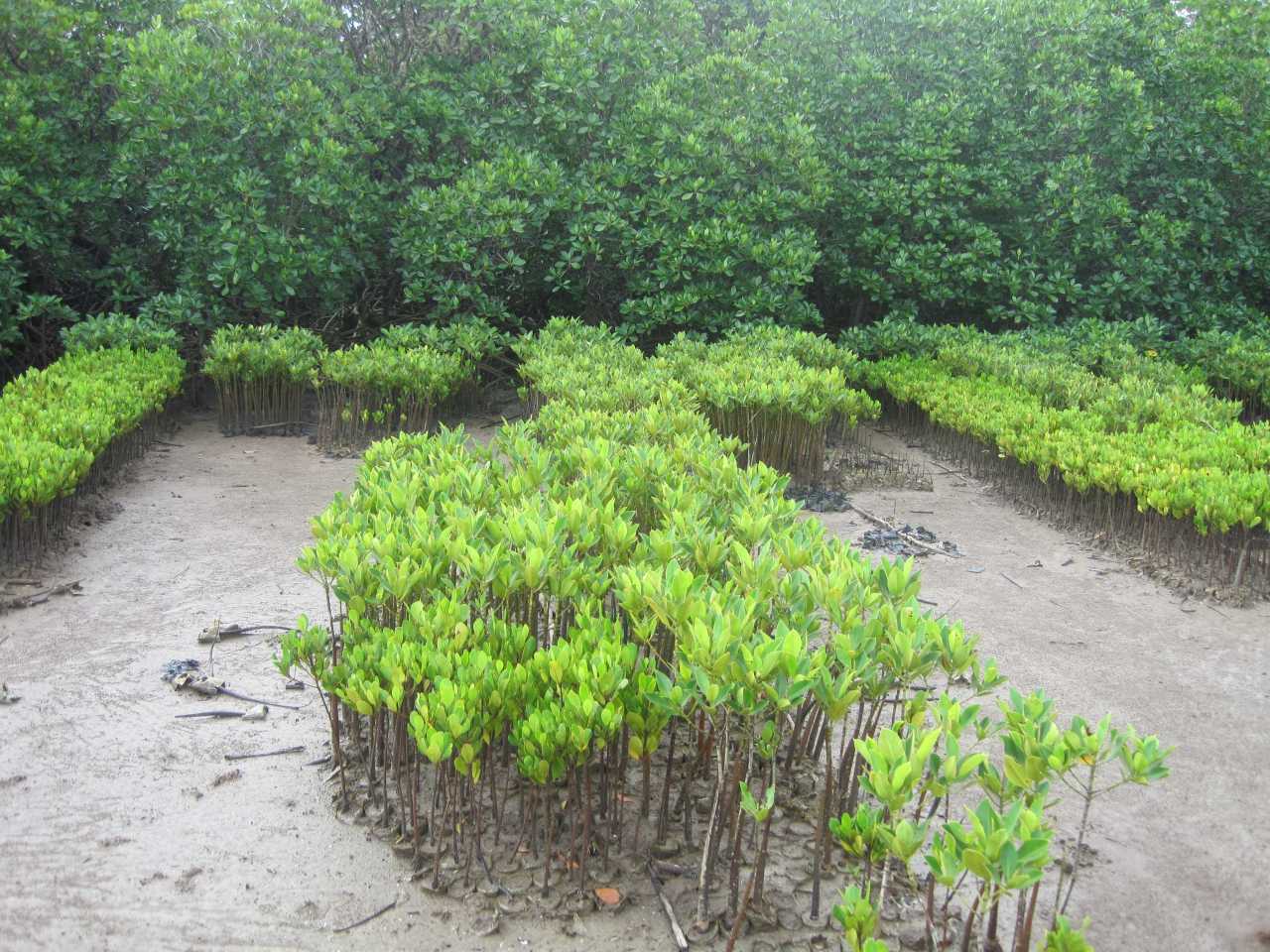
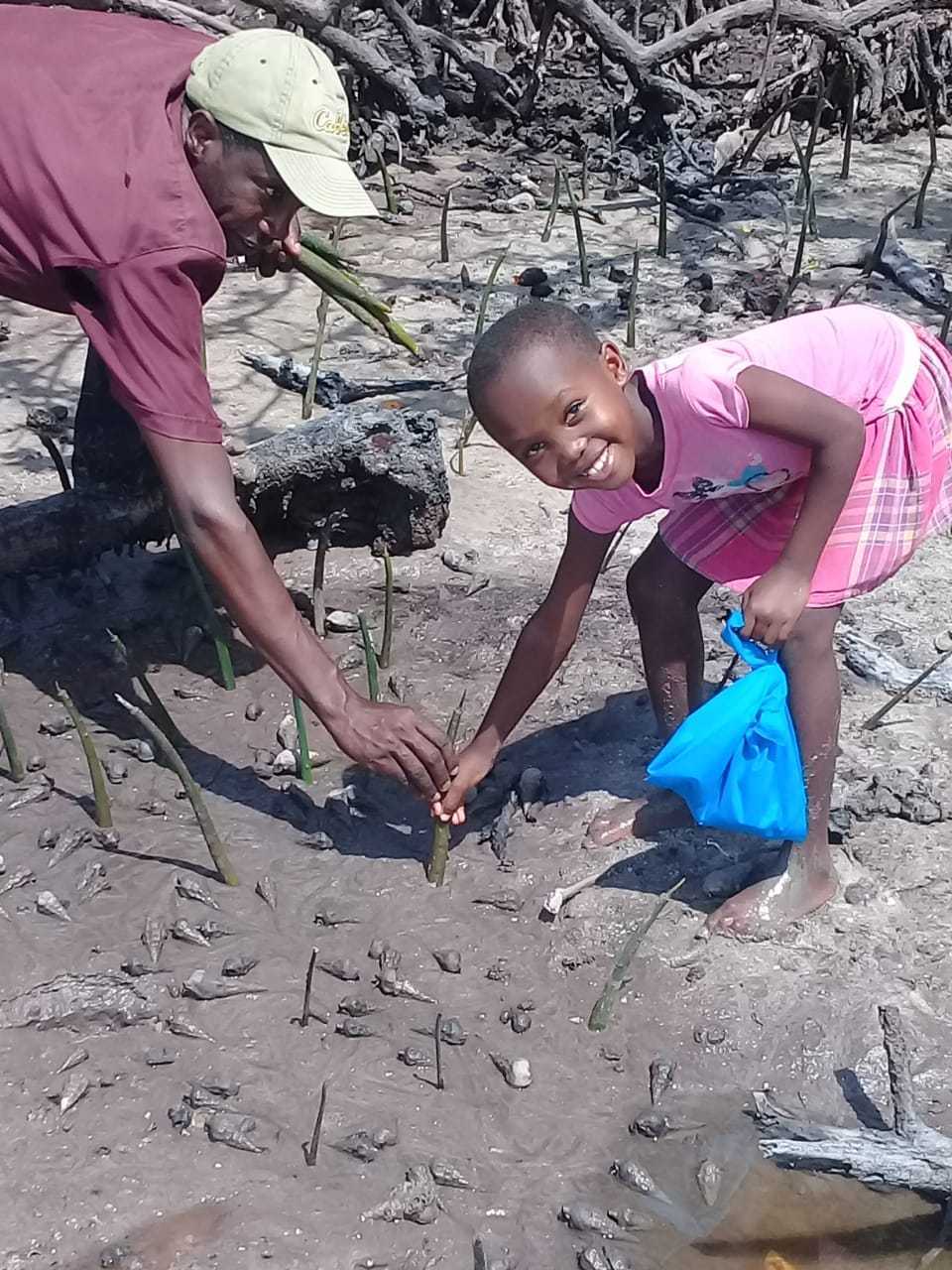
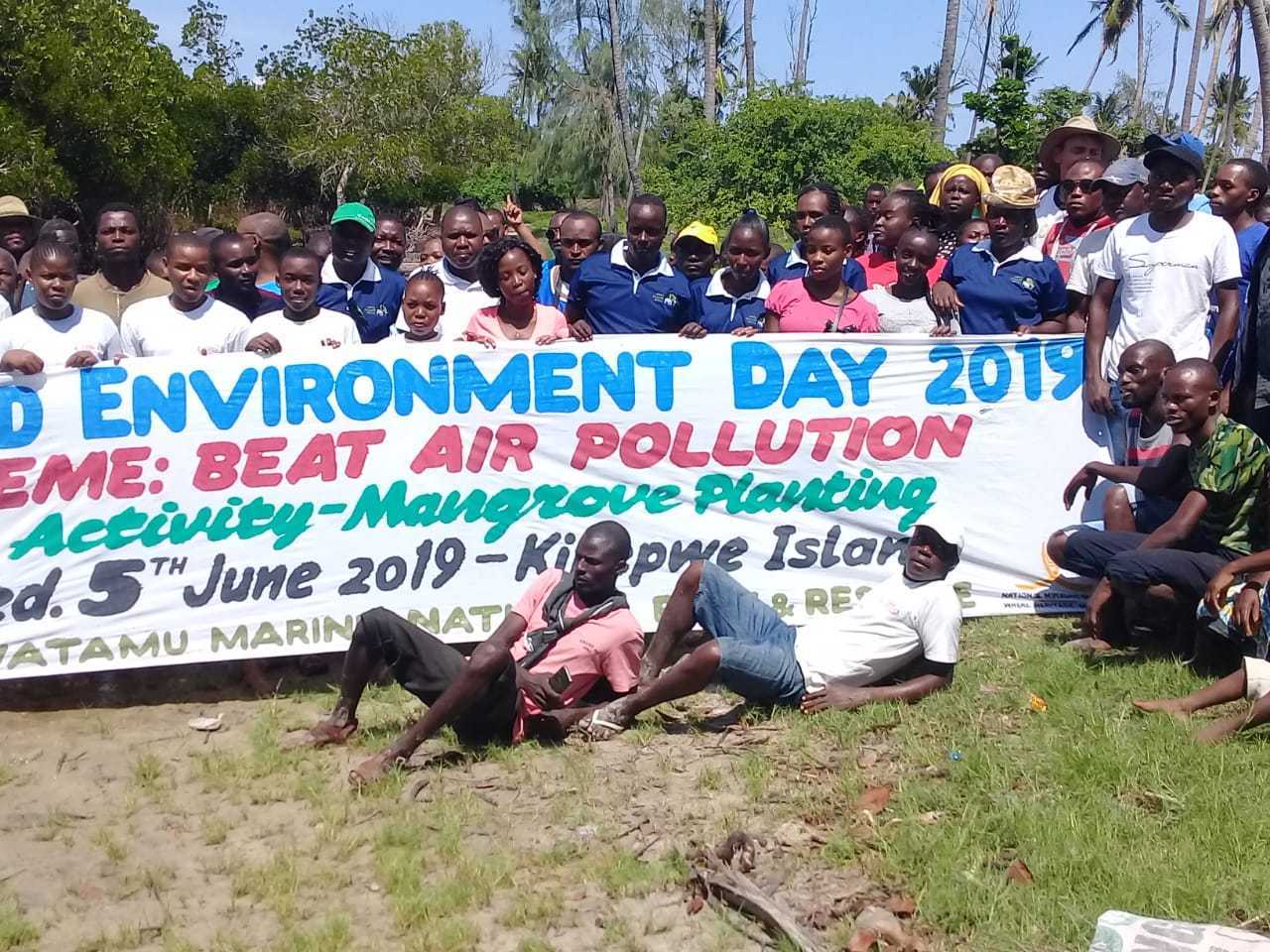
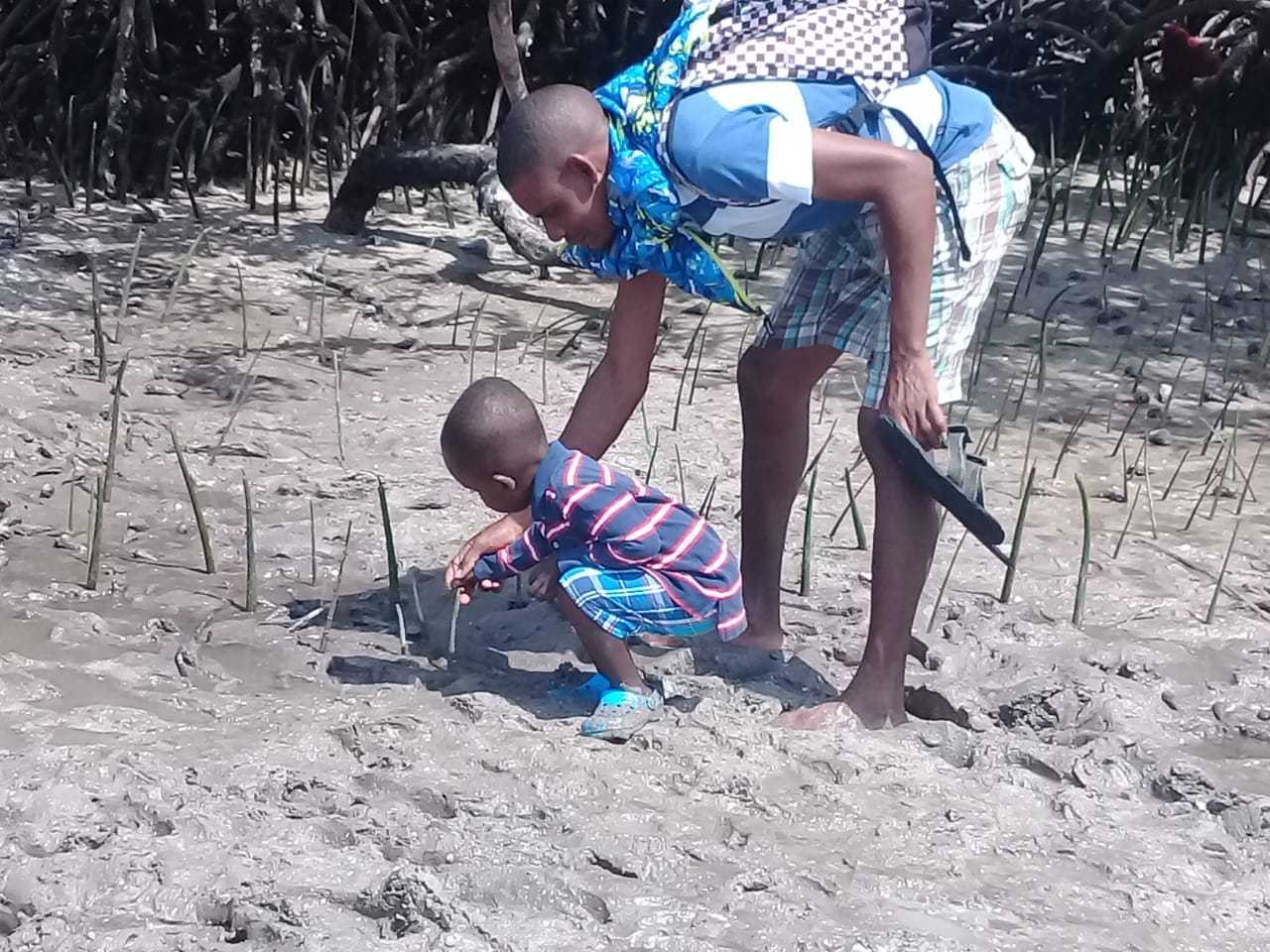
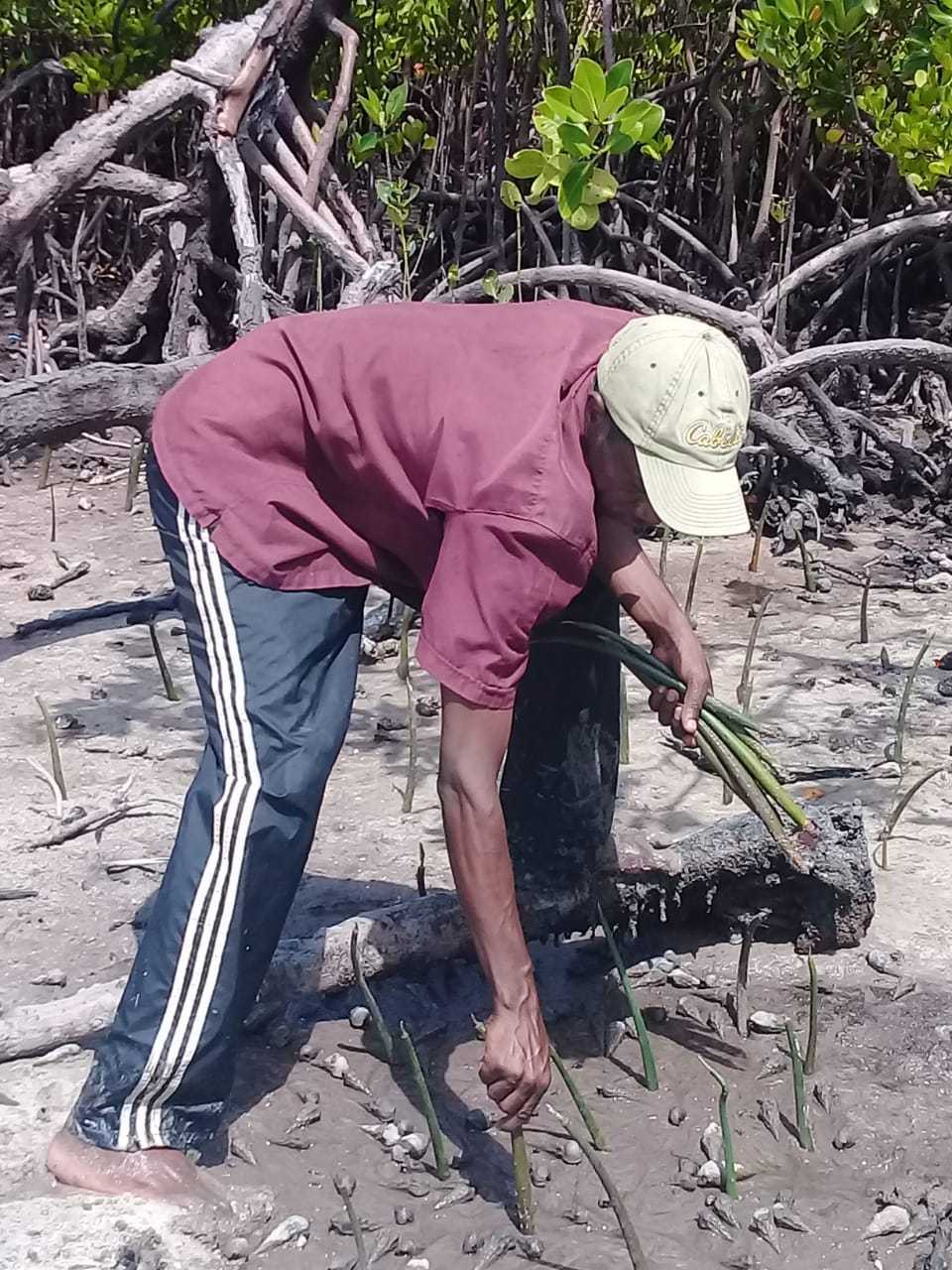
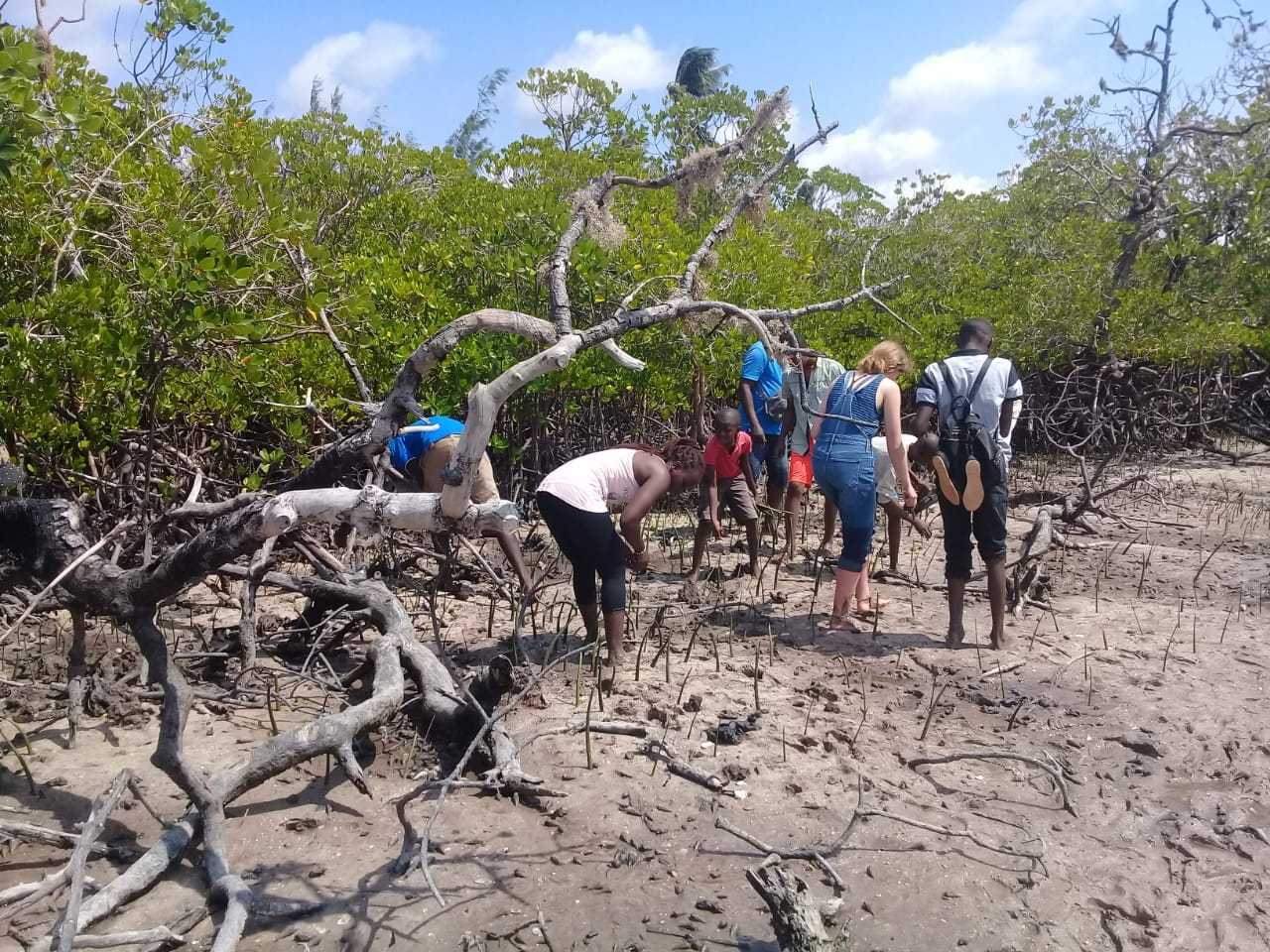
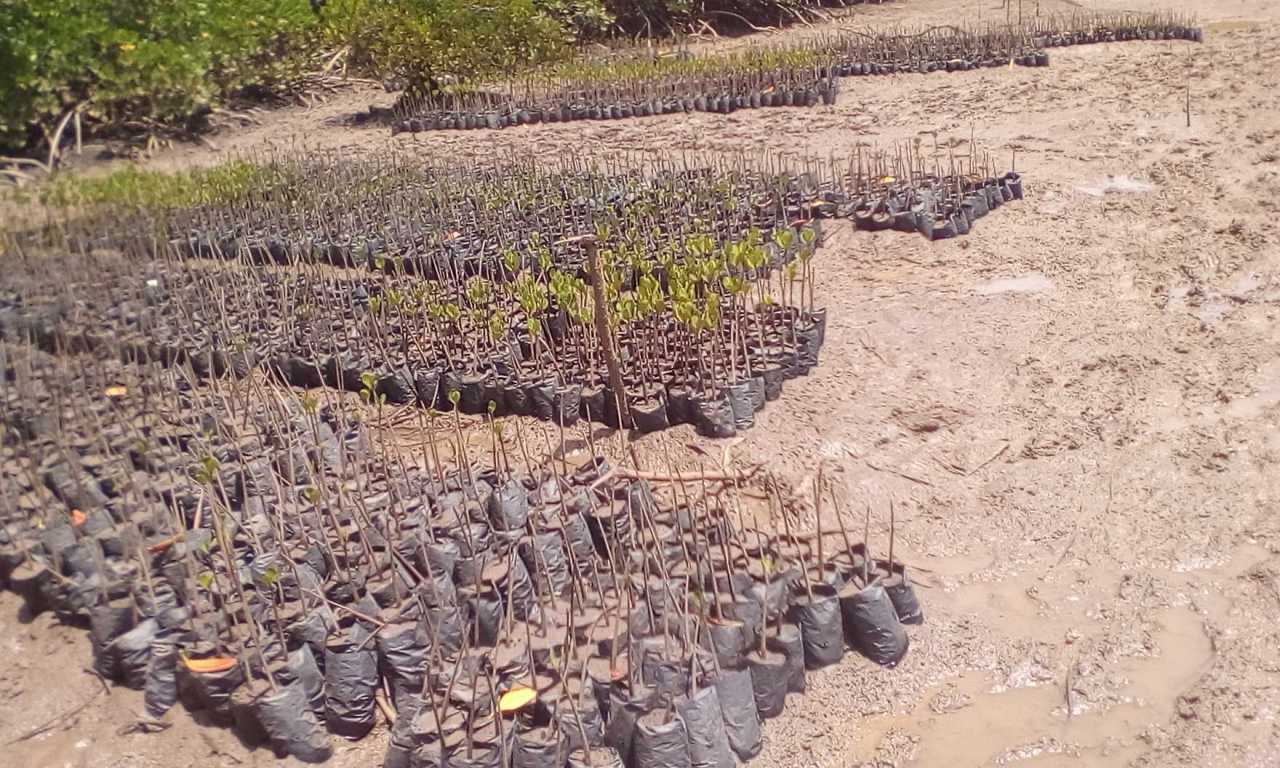
Cobec Kenya is an environmental NGO that protects coastal areas and the species that inhabit them, including sea turtles. We're a not-for-profit and urgently seek financial assistance to restore the habitat of these magnificent endangered creatures by planting mangroves.
Threats to Mangroves
Key threats to mangroves in the seascape include over-exploitation of wood and non-wood products, conversion of mangroves areas to other land uses such as rice farming, infrastructure development, pollution effects and sedimentation. Climate change is also to some extent affecting the remaining mangroves, particularly through sea-level rise, aridity and influx of freshwater causing floods and sedimentation. Key drivers leading to deterioration of mangroves in the seascape has been lack of cohesion among stakeholders in the use and management of the resource. This has been exacerbated by a lack of recognition of customary rules and indigenous knowledge in governing subsistent use of mangrove resources.
The total area of mangroves in the Kenya is estimated at 61,271 ha, with 8,354 ha or 14% of the total mangrove coverage being in Kwale County in which Shimoni-Vanga lie. An overarching problem facing the seascape is environmental degradation due to weak community organizational capacity in collective decision making and action in building and maintaining the resilience of these socio-ecological landscapes.
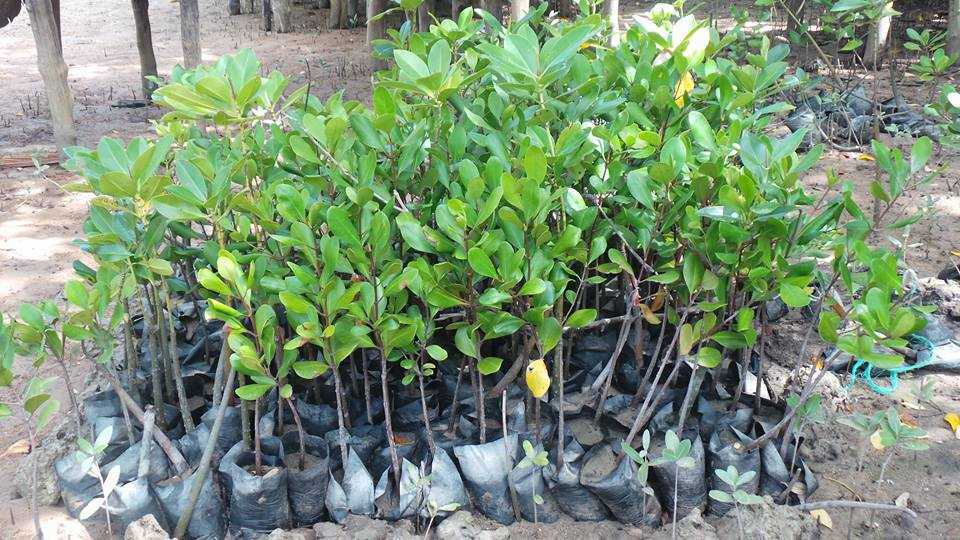
The Need for Reforestation
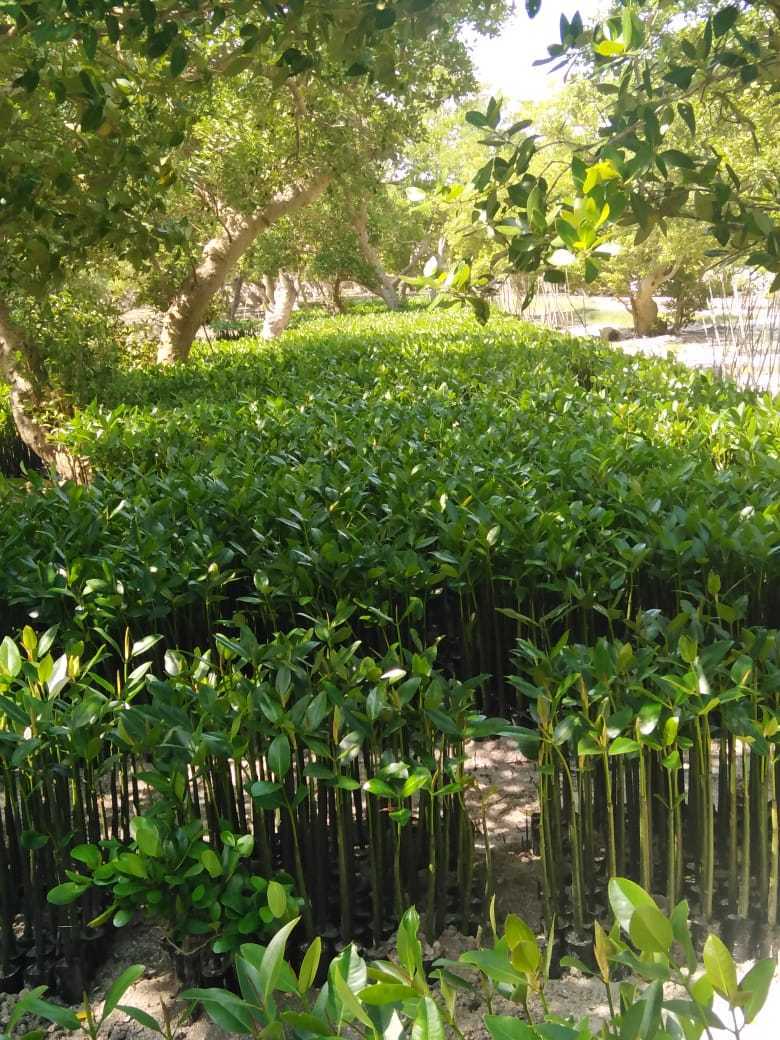
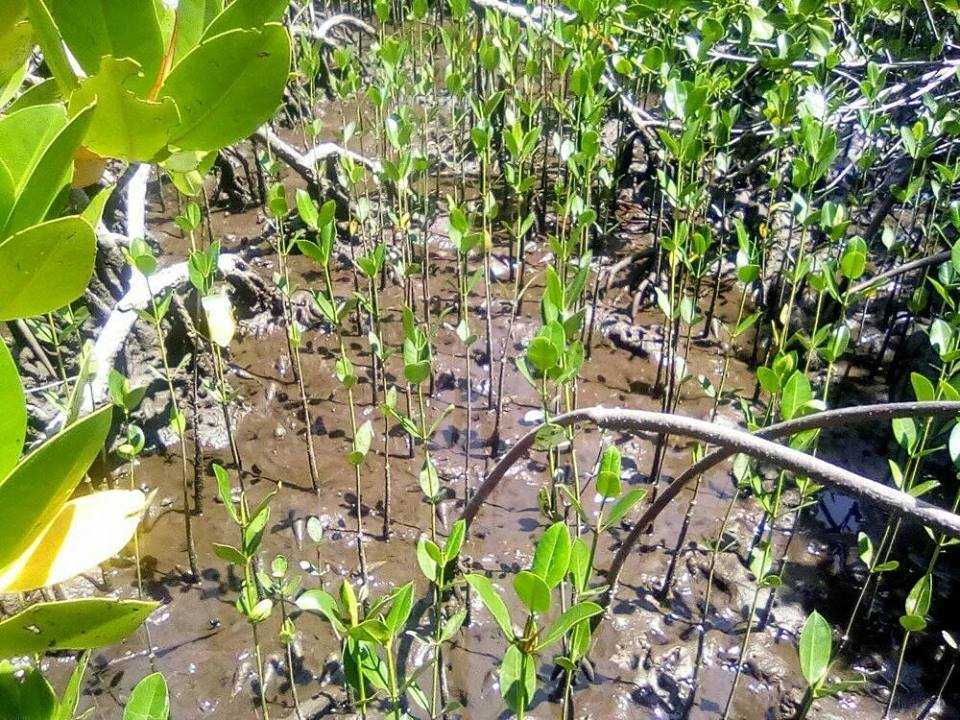
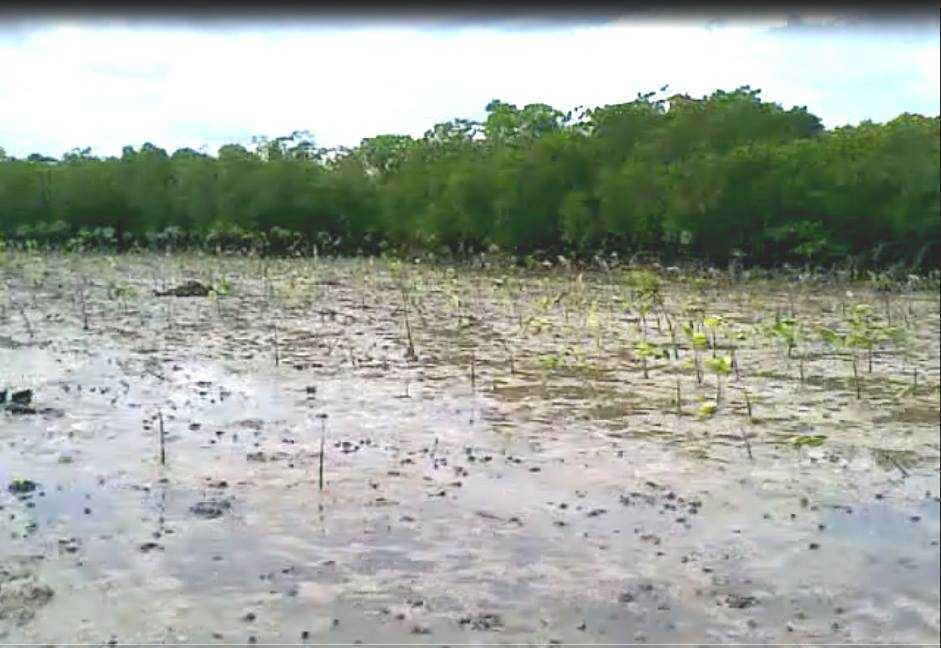
Mangrove forests are coastal plant communities that are part of a larger coastal ecosystem that typically includes mud flats, seagrass meadows, tidal marshes, salt barrens and even coastal upland forests and freshwater wetlands (i.e. peatlands), freshwater streams and rivers. In more tropical climates coral reefs may also be part of this ecosystem. Reforestation is needed because mangroves are critical habitat for many species of fish and wildlife. They also serve as coastal fish and shellfish nursery habitat, and produce large quantities of leaf material that are the basis for a detritus food web (Hamilton and Snedaker 1984, Lewis et al. 1985). Mangroves also serve as coastal protection from hurricanes and typhoons, and riverine mangroves help remove pollutants before they enter adjacent coastal waters. Despite their documented ecological functions, mangrove forests have been dredged and filled for decades to provide for other coastal uses, including ports and housing.
Below is a short video of some of our mangrove planters hard at work!